使用 HAL 和 JSON 视图
了解如何使用 Grails 构建可发现的 API
作者: ZacharyKlein
Grails 版本 5.0.1
1 Grails 培训
Grails 培训 - 由 Grails 框架的创建者和积极维护者开发和提供!
2 入门
超文本应用语言 (HAL) 是 JSON 或 XML 代码中定义超媒体(如指向外部资源的链接)的互联网草案(“正在进行中的工作”)标准约定。
HAL 的目的是使 API “可发现” - 它定义了一组允许 API 使用者在资源之间遵循链接的约定,以及为“探索”API 提供分页和其他便利功能的约定。HAL 是用于实现 HATEOAS(超媒体作为应用状态的引擎)架构的流行标准,它是基本 REST 架构的扩展。
| 要全面了解 HAL,请查看以下 URL 上的概述和规范:http://stateless.co/hal_specification.html |
Grails 通过 JSON 视图(Grails Views 库的一部分)提供对 HAL 的支持。可以在已有应用中使用该库,具体按照文档中的安装步骤操作,也可以使用 `rest-api` 配置文件或扩展 `rest-api` 配置文件的某个前端配置文件 (`angular`、`angular2` 和 `react`) 创建一个新应用。
在本指南中,我们在 `initial` 项目中提供了一个使用 `rest-api` 配置文件的 Grails 5.0.1 基本应用。我们还包含了一些要通过我们的 API 公开的领域类。可以自行生成项目(在这种情况下,需要将领域类从 `initial/grails-app/domain/` 复制到自己的项目中),或简单地使用 `initial` 项目来遵循指南。
2.1 您需要什么
要完成本指南,您需要以下内容
-
一些时间
-
一个好的文本编辑器或 IDE
-
安装JDK 1.8 或更高版本,并配置好 JAVA_HOME
2.2 如何完成本指南
要开始,请执行以下操作
-
下载并解压源代码
或
-
克隆 Git 仓库
git clone https://github.com/grails-guides/using-hal-with-json-views.git
Grails 指南仓库包含两个文件夹
-
initial初始项目。通常是一个简单的 Grails 应用,有一些附加代码,可以帮助您快速入门。 -
complete一个完成的示例。它是处理指南中提供的步骤并将这些更改应用于 `initial` 文件夹的结果。
要完成本指南,请转到 `initial` 文件夹
-
cd至grails-guides/using-hal-with-json-views/initial
并按照下一部分中的说明操作。
如果您 cd 进入 grails-guides/using-hal-with-json-views/complete,则可以直接转到完成的示例 |
3 运行应用
Grails 为 RESTful URL 映射提供出色的支持,以公开领域资源。在 `initial` 项目中,我们已经使用 `@Resource` 注解对领域类进行了注释,该注解生成一个 `RestfulController` 和关联的 URL 映射,以将每个领域类公开为一个 RESTful 资源。
package com.example
import grails.rest.*
@Resource(readOnly = true, uri='/api/customers') (1)
class Customer {| 1 | @Resource 注解采用多个可选参数,包括 URL 端点和格式选项,以及 API 是否只公开读取端点 |
将这些注解添加到领域类,可以给我们创建一个 API 的良好开端。请参阅 Grails 文档,了解有关 `@Resource` 的更多信息
要运行应用,请使用命令 ./gradlew bootRun,该命令会在端口 8080 上启动应用。
现在 Grails 应用程序已运行,我们可以通过 @Resource 注解尝试 Grails 为我们生成的 API。对 /api/products 发出 GET 请求以获取产品列表
curl -H "Accept: application/json" localhost:8080/api/products'''
[
{
"id": 1,
"category": {
"id": 1
},
"inventoryId": "CLOTH001",
"name": "Cargo Pants",
"price": 15.00
},
{
"id": 2,
"category": {
"id": 1
},
"inventoryId": "CLOTH002",
"name": "Sweater",
"price": 12.00
},
{
"id": 3,
"category": {
"id": 1
},
"inventoryId": "CLOTH003",
"name": "Jeans",
"price": 15.00
},
{
"id": 4,
"category": {
"id": 1
},
"inventoryId": "CLOTH004",
"name": "Blouse",
"price": 18.00
},
{
"id": 5,
"category": {
"id": 1
},
"inventoryId": "CLOTH005",
"name": "T-Shirt",
"price": 10.00
},
{
"id": 6,
"category": {
"id": 1
},
"inventoryId": "CLOTH006",
"name": "Jacket",
"price": 20.00
},
{
"id": 7,
"category": {
"id": 2
},
"inventoryId": "FURN001",
"name": "Bookcase",
"price": 40.00
},
{
"id": 8,
"category": {
"id": 2
},
"inventoryId": "FURN002",
"name": "Coffee Table",
"price": 50.00
},
{
"id": 9,
"category": {
"id": 2
},
"inventoryId": "FURN003",
"name": "Vanity",
"price": 90.00
},
{
"id": 10,
"category": {
"id": 3
},
"inventoryId": "TOOL001",
"name": "Table Saw",
"price": 120.00
}
]
'''
//...
]在此处,对 /api/orders/1 发出 GET 请求会返回 id 为 1 的 Order
curl -H "Accept: application/json" localhost:8080/api/orders/1'''
{
"id" : 1,
"shippingAddress" : {
"id" : 1
},
"shippingCost" : 13.54,
"orderId" : "0A12321",
"orderPlaced" : "2017-02-08T09:10:36Z",
"products" : [
{
"id" : 11
},
{
"id" : 6
},
{
"id" : 1
}
],
"customer" : {
"id" : 1
}
}
'''由于我们在 @Resource 注解中指定了 readOnly = true,Grails 不会生成更新/创建/删除操作的终结点。这对本指南中的步骤来说已经足够,但您可以移除 readOnly 属性 (或将其设置为 false) 以启用“写入”操作。 |
4 构建我们的 API
Grails 渲染的默认 JSON 很棒,但它不一定能表达我们的面向公众的 API 中我们想要了解的详细信息。JSON 视图让我们能够在经过静态编译的 Groovy 视图中使用 Groovy 的 StreamingJsonBuilder 渲染我们的数据。JSON 视图提供了一种基于 DSL 的强大工具,用于表达我们 API 的 JSON 输出。
4.1 介绍 JSON 视图
以下是 JSON 视图的一个简单示例
json.message {
hello "world"
}渲染后,此 JSON 视图将生成以下输出
{"message":{ "hello":"world"}}JSON 视图还支持 model,它引用传送到视图的数据,如下所示
model {
String message
}
json.message {
hello message
}JSON 视图是具有文件扩展名 gson 的 Groovy 文件,它们驻留在 grails-app/views 目录中,就像 GSP 视图一样。按照约定,它们会被解析为与视图目录同名的控制器,再次如同 GSP 视图一样。
4.2 自定义我们的 API
让我们创建一个 JSON 视图来自定义来自 /api/orders/$id 终结点的输出。目前,默认 JSON 渲染器包括所有关联对象的 id。但是,我们不希望公开 shippingAddress 属性的 id(它是我们的 Address 域类的一个实例)——它没有在我们的 API 中作为一个域资源公开,并且仅与 Order 或 Customer 中作为 API 用户相关。理想情况下,我们希望在 Order API 的 JSON 输出中包括 shippingAddress 字段。
此外,我们希望将 orderId 属性表示为订单的 id,而不是数据库中的实际 id。
在 grails-app/views 下创建名为 order 的新目录
$ mkdir grails-app/views/order如果您熟悉 Grails 的视图解析,您可能会认为我们必须创建 OrderController 才能使用我们 order 目录中的视图。我们可以这样做,但是由于我们正在使用我们域类上的 @Resource 注解,所以 Grails 会为我们生成一个关联的 OrderController(它会继承自 RestfulController)。所以,在这一点上,我们不需要为我们的 Order 类创建控制器。 |
创建新的 JSON 视图,名为 show.gson。它将解析到控制器中的 show 操作,一如在普通 Grails 应用程序中 show.gsp 页面所做的那样。编辑带有以下内容的新视图
import com.example.Order
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat('M-dd-yyy')
model {
Order order
}
json {
id order.orderId
shippingCost order.shippingCost
date simpleDateFormat.format(order.orderPlaced)
shippingAddress { (1)
street order.shippingAddress.street
street2 order.shippingAddress.street2
city order.shippingAddress.city
state order.shippingAddress.state
zip order.shippingAddress.zip
}
products order.products.collect { [id: it.id] } (2)
customer {
id order.customer.id
}
}| 1 | 在本文,我们使用 Address 类中的字段填充 shippingAddress |
| 2 | 请注意,我们正在使用 collect 方法对集合 (order.products) 进行迭代并返回一个映射 - 它将创建一个 JSON 对象数组 |
现在,如果您向 /api/orders/1 发起请求,您应该看到以下输出
curl -H "Accept: application/json" localhost:8080/api/orders/1{
id: "0A12321",
shippingCost: 13.54,
date: "2-08-2017",
shippingAddress: {
street: "321 Arrow Ln",
street2: null,
city: "Chicago",
state: "IL",
zip: 646465
},
products: [
{
id: 11
},
{
id: 1
},
{
id: 6
}
],
customer: {
id: 1
}
}让我们为 Customer 域类创建另一个 JSON 视图。在 grails-app/views 下创建名为 customer 的新目录,以及 show.gson 新 JSON 视图
$ mkdir grails-app/views/customer创建新的 JSON 视图,名为 show.gson。它将解析到控制器中的 show 操作,一如在普通 Grails 应用程序中 show.gsp 页面所做的那样。编辑带有以下内容的新视图
import com.example.Customer
model {
Customer customer
}
json {
id customer.id
firstName customer.firstName
lastName customer.lastName
fullName "${customer.firstName} ${customer.lastName}"
address {
street customer.address.street
street2 customer.address.street2
city customer.address.city
state customer.address.state
zip customer.address.zip
}
orders customer.orders.collect { [id: it.id] }
}5 使我们的 API 通过 HAL 可发现
现在,我们已经略微自定义了我们的 API,但是我们有一些问题
-
通过自定义订单的
id属性,对于客户端来说,引用特定记录不再明确(因为我们的 API 仍然依赖数据库 id) -
我们公开的三个域类拥有许多只公开 id 的关联 - 这意味着客户端需要发起新请求来获取关联对象(例如,消耗订单的客户端需要发起单独的请求以获取其产品的字段)
-
我们的 API 是相当生僻的 - 缺少文档,我们的 API 用户需要猜测端点才能到达关联记录。即使有文档,客户端可能需要使用自定义代码来浏览我们的 API,毫无一致的标准可遵循。
HAL+JSON 标准的惯例可以帮助我们解决这些问题,而 JSON 视图为 HAL 提供了一流的支持 - 让我们看看我们如何使用它。
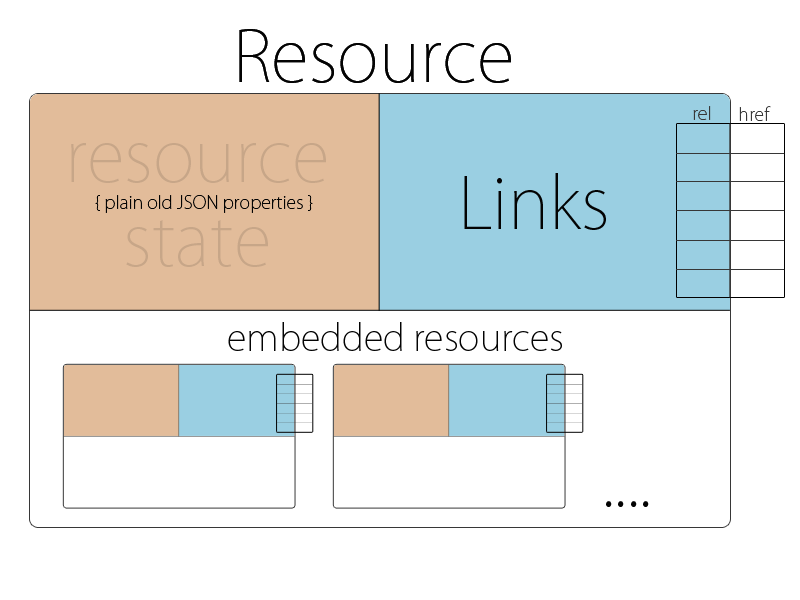
5.1 链接资源
链接是 HAL 标准中的关键。HAL 资源包括一个名为 _links 的特殊字段,它包含一个 JSON 对象数组,其中定义了到相关资源的链接。HAL 链接(至少)包含两条信息 - 关系和包含访问相关资源的 URL 的 href。还可以包括其他元数据。
以下是一个具有 _links 字段和两个链接的 JSON 正文示例
{
title: "Groovy Recipes",
author: "Scott Davis",
pages: 100,
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:8080/book/show/1", (1)
},
"author": {
"href": "https://:8080/author/show/1", (2)
}
}
}| 1 | self 是每个 HAL 资源都应该包括的特殊链接 - 它指定指向当前资源的 URL "返回"。 |
| 2 | 在这里,我们定义了一个名为 author 的自定义链接,它指定了 author 字段的 URL |
当客户端访问 HAL 资源时,可以"浏览" _links 字段中表示的关系,而无需客户端知道 API 端点的确切构成。
//examples are using the fetch API: https://mdn.org.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API
//retrieve a book instance from the API
fetch("https://:8080/api/book/1").then(function(response) {
return response.json();
}).then(function(data) {
this.book = data;
});
//retrieve book's author using links
var author;
fetch(book._links.author.href).then(function(response) {
return response.json();
}).then(function(data) {
author = data;
});JSON 视图实现了 Groovy 特性 HalView,它通过多种方法显示了符合 HAL 的 JSON 的 hal 辅助对象。其中之一是 links 方法
model {
Order order
}
json {
hal.links(order)
//...
}在我们的域资源中调用 hal.links() 会生成下列 JSON 输出
{
_links: {
self: {
href: "https://:8080/api/orders/1",
hreflang: "en_US",
type: "application/hal+json"
}
}
}让我们修改 order/show.gson 视图,添加一个 self 链接和一个指向关联客户的链接
import com.example.Order
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat('M-dd-yyy')
model {
Order order
}
json {
hal.links(self: order, customer: order.customer) (1)
id order.orderId
shippingCost order.shippingCost
date simpleDateFormat.format(order.orderPlaced)
shippingAddress {
street order.shippingAddress.street
street2 order.shippingAddress.street2
city order.shippingAddress.city
state order.shippingAddress.state
zip order.shippingAddress.zip
}
products order.products.collect { [id: it.id] }
customer {
id order.customer.id
}
}| 1 | links 方法可以接受一个域资源实例或一个链接名称和要链接的对象的映射。 |
向 https://:8080/api/orders/1 发送请求
{
_links: {
self: {
href: "https://:${serverPort}/api/orders?id=1",
hreflang: "en",
type: "application/hal+json"
},
customer: {
href: "https://:${serverPort}/api/customers?id=1",
hreflang: "en",
type: "application/hal+json"
}
},
id: "0A12321",
shippingCost: 13.54,
date: "2-08-2017",
shippingAddress: {
street: "321 Arrow Ln",
street2: null,
city: "Chicago",
state: "IL",
zip: 646465
},
products: [
{
id: 11
},
{
id: 1
},
{
id: 6
}
],
customer: {
id: 1
}
}
//...
}5.2 用模板呈现集合
Order 包含与 Product 的一多关系,现在,我们的 API 将标识 ID 的一个简单列表作为订单中的产品进行返回。理想情况下,我们希望同时包括指向这些产品的链接,以便我们 API 的客户端可以通过我们提供的链接检索每个产品的详细信息。我们可以使用 JSON 视图的模板功能。
在 grails-app/views/order 目录中,创建一个名为 _product.gson 的新 JSON 模板
import com.example.Product
model {
Product product
}
json {
hal.links(product)
id product.id
}现在,在 order/show.gson 视图中,我们可以使用新的 _product 模板将 order.products 传递给 tmpl 辅助对象
import com.example.Order
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat('M-dd-yyy')
model {
Order order
}
json {
hal.links(self: order, customer: order.customer)
id order.orderId
shippingCost order.shippingCost
date simpleDateFormat.format(order.orderPlaced)
shippingAddress {
street order.shippingAddress.street
street2 order.shippingAddress.street2
city order.shippingAddress.city
state order.shippingAddress.state
zip order.shippingAddress.zip
}
products tmpl.product(order.products) (1)
}| 1 | tmpl 辅助对象将方法名称解析为当前视图目录中的模板 - 例如,tmpl.product 将解析为 /order/_product.gson。如果你想要从当前目录之外访问模板,你可以将绝对路径(相对于 views 目录)作为字符串使用:tmpl."/customer/order"() 将解析为 grails-app/views/customer/_order.gson。 |
| 欲了解更多有关在 JSON 视图中使用模板的信息,请参阅 Grails 视图文档。 |
向 https://:8080/api/orders/1 发送请求,你应该会看到 products 数组中每个产品的 _links
{
_links: {
self: {
href: "https://:${serverPort}/api/orders?id=1",
hreflang: "en",
type: "application/hal+json"
},
customer: {
href: "https://:${serverPort}/api/customers?id=1",
hreflang: "en",
type: "application/hal+json"
}
},
id: "0A12321",
shippingCost: 13.54,
date: "2-08-2017",
shippingAddress: {
street: "321 Arrow Ln",
street2: null,
city: "Chicago",
state: "IL",
zip: 646465
},
products: [
{
_links: {
self: {
href: "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/11",
hreflang: "en",
type: "application/hal+json"
}
},
id: 11
},
{
_links: {
self: {
href: "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/6",
hreflang: "en",
type: "application/hal+json"
}
},
id: 6
},
{
_links: {
self: {
href: "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/1",
hreflang: "en",
type: "application/hal+json"
}
},
id: 1
}
]
}让我们对 Customer 的订单 使用同样的技术 - 在 `grails-app/views/customer/_order.gson` 处创建一个新模板
import com.example.Order
model {
Order order
}
json {
hal.links(order)
id order.id
}修改 customer/show.gson 视图以使用新的 _order 模板
让我们对 Customer 的订单 使用同样的技术 - 在 `grails-app/views/customer/_order.gson` 处创建一个新模板
import com.example.Customer
model {
Customer customer
}
json {
id customer.id
firstName customer.firstName
lastName customer.lastName
fullName "${customer.firstName} ${customer.lastName}"
address {
street customer.address.street
street2 customer.address.street2
city customer.address.city
state customer.address.state
zip customer.address.zip
}
orders tmpl.order(customer.orders)
}5.3 嵌入关联对象
让我们看看 Product 域资源。Product 与 Category 具有 belongsTo 关系,该关系在我们的默认 JSON 输出中以一个包含类别 ID 的简单对象方式表达
{
id: 1,
category: {
id: 1
},
inventoryId: "CLOTH001",
name: "Cargo Pants",
price: 15
}我们希望让 API 的使用者可以更轻松地获取产品的类别。我们有几个选项
-
我们可以简单地 在我们的 JSON 视图中包括
category详细信息:此方法会模糊 API 中Product和Category资源之间的界限 - 它会给客户端错误的印象,即category.name是Product的一个属性,而不仅仅只是本身的 API 资源。 -
我们可以提供一个指向分类的链接:此方法要求客户端发出新的请求才能获取分类的详细信息,而且大多数客户端可能都希望在同一个请求中同时获取产品和分类的详细信息。
你可能还记得,对于订单的shippingAddress,我们采用了这两种方法中的一种(在 JSON 视图中包括关联对象的详细信息),这是因为在我们的 API 中并未将Address公开为资源,因此就我们的 API 而言,Address实际上是Order(shippingAddress)或Customer(address)的一部分。 |
HAL 指定使用_embedded属性以嵌套格式表示跨资源关联关系。使用嵌入方法,我们可以在同一个 HAL+JSON 响应中包含Category,但是分类将位于一个单独的元素中,以明确它们是单独的资源。
JSON 视图通过hal帮助程序提供embedded方法,该方法会在我们的 JSON 视图中生成一个_embedded元素。它将包括嵌入对象的默认 JSON 输出以及每个对象的_self链接。让我们使用此方法将分类嵌入到我们的产品输出中。
在grails-app/views下创建名为product的新目录
$ mkdir grails-app/views/product/在这个目录下创建一个名为show.gson的新 JSON 视图
import com.example.Product
model {
Product product
}
json {
hal.links(product)
hal.embedded(category: product.category) (1)
id product.inventoryId
name product.name
price product.price
}| 1 | 我们将embedded方法传递一个元素名称映射(在本例中为category),映射到要嵌入的对象(product.category) |
现在向https://:8080/api/products/1发送请求
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/1",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"_embedded": {
"category": {
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/categories/1",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Clothing",
"version": 0
}
},
"id": "CLOTH001",
"name": "Cargo Pants",
"price": 15.00
}在前面的代码片段中,category对象包括为我们的Category资源输出的默认 JSON 呈现器输出,以及一个_self链接,以便客户端在需要时可以直接请求分类。
让我们在order/show.gson视图中使用embedded方法,并嵌入order.customer资源
import com.example.Order
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat('M-dd-yyy')
model {
Order order
}
json {
hal.links(self: order, customer: order.customer)
hal.embedded(customer: order.customer) (1)
id order.orderId
shippingCost order.shippingCost
date simpleDateFormat.format(order.orderPlaced)
shippingAddress {
street order.shippingAddress.street
street2 order.shippingAddress.street2
city order.shippingAddress.city
state order.shippingAddress.state
zip order.shippingAddress.zip
}
products tmpl.product(order.products)
}向 https://:8080/api/orders/1 发送请求
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/orders?id=1",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
},
"customer": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/customers?id=1",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"_embedded": {
"customer": {
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/customers/1",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"firstName": "Peter",
"lastName": "River",
"version": 0
}
},
"id": "0A12321",
"shippingCost": 13.54,
"date": "2-08-2017",
"shippingAddress": {
"street": "321 Arrow Ln",
"street2": null,
"city": "Chicago",
"state": "IL",
"zip": 646465
},
"products": [
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/6",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"id": 6
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/11",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"id": 11
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/1",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"id": 1
}
]
}现在,我们的 API 客户端可以访问嵌入资源的详细信息,而无需发出其他请求了。
//examples are using the fetch API: https://mdn.org.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API
//retrieve an order instance from the API
fetch("https://:8080/api/orders/1").then(function(response) {
return response.json();
}).then(function(data) {
this.order = data;
});
var customer = this.order._embedded.customer;
console.log("Order ID: " + this.order.id);
console.log("Customer: " + customer.firstName + " " + customer.lastName);
//retrieve a product instance from the API
fetch("https://:8080/api/products/1").then(function(response) {
return response.json();
}).then(function(data) {
this.product = data;
});
console.log("Product: " + this.product.name);
console.log("Category:" + this.order._embedded.category.name);5.4 分页结果
HAL 标准指定的另一个约定是分页。在提供资源列表时,_links元素可以提供first、prev、next和last链接,可用于浏览资源列表。
hal帮助程序提供paginate方法,该方法将生成这些链接并处理资源分页。此方法需要在 JSON 视图的model中获得更多信息,以便跟踪当前的偏移量、每页的最大记录数和总资源数。为此,我们需要创建一个控制器,以便我们可以传入所需的模型参数。
让我们在我们的 Product 资源上使用 HAL 分页链接。
由于我们将创建我们自己的 ProductController 来提供分页所需的参数,我们需要在我们 Product 领域类上一直在使用的 @Resource 注解。编辑 grails-app/domain/com/example/Product.groovy
package com.example
class Product {
String name
String inventoryId
BigDecimal price
static belongsTo = [ category : Category ]
}您经常会发现,在开发 RESTful API 时,由 @Resource 生成的控制器和 URL 映射是开始的好方法,但在某些时候您会希望对该 API 有更多控制权 - 在此点上,自己生成 RestfulController 是一个好的解决方案。 |
现在,使用 create-restful-controller 命令(由 rest-api 配置文件提供)创建一个新的 RestfulController
$ ./grailsw create-restful-controller com.example.ProductController使用以下内容编辑此新控制器
package com.example
import grails.rest.RestfulController
class ProductController extends RestfulController<Product> {
static responseFormats = ['json']
ProductController() {
super(Product)
}
@Override
def index(Integer max) {
params.max = Math.min(max ?: 10, 100)
return [
productList : listAllResources(params), (1)
productCount: countResources(), (2)
max : params.max, (3)
offset : params.int("offset") ?: 0, (4)
sort : params.sort, (5)
order : params.order (6)
]
}
@Override
boolean getReadOnly() {
return true
}
}| 1 | listAllResource() 是由 RestfulController 提供的一个方法,用于返回所有领域资源列表 - 您可以覆盖此方法,以控制生成此列表的方式 |
| 2 | countResources() 是另一个 RestfulController 方法 - 同样,您可以覆盖其实现,以适合您的 API |
| 3 | 每页的总结果数 |
| 4 | 偏移量(用于计算当前页) |
| 5 | 按其排序的属性 |
| 6 | 排序的方向 |
最后,我们需要编辑我们的 UrlMappings 以创建以前使用 @Resource 注解生成的 rest 端点。格雷耳支持 URL 映射上的一个 resource 属性,它将自动生成这些 URL。编辑 UrlMappings.groovy,并将以下规则添加到 mappings 块
"/api/products"(resources: "product")现在,我们可以使用分页创建我们的新 JSON 视图。在 grails-app/views/product 中创建以下视图和模板
import com.example.Product
model {
Iterable<Product> productList (1)
Integer productCount (2)
Integer max
Integer offset
String sort
String order
}
json {
hal.paginate(Product, productCount, offset, max, sort, order) (3)
products tmpl.product(productList ?: [])
count productCount
max max
offset offset
sort sort
order order
}| 1 | 产品资源列表 |
| 2 | 来自我们控制器的分页参数 |
| 3 | 在此,我们将分页参数传递给 paginate 方法,该方法将生成 HAL 分页链接 |
import com.example.Product
model {
Product product
}
json {
hal.links(product)
name product.name
id product.inventoryId
price product.price
category product.category.name
}"""
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products?offset=0&max=10",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
},
"first": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products?offset=0&max=10",
"hreflang": "en"
},
"next": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products?offset=10&max=10",
"hreflang": "en"
},
"last": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products?offset=10&max=10",
"hreflang": "en"
}
},
"products": [
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/1",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Cargo Pants",
"id": "CLOTH001",
"price": 15.00,
"category": "Clothing"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/2",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Sweater",
"id": "CLOTH002",
"price": 12.00,
"category": "Clothing"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/3",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Jeans",
"id": "CLOTH003",
"price": 15.00,
"category": "Clothing"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/4",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Blouse",
"id": "CLOTH004",
"price": 18.00,
"category": "Clothing"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/5",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "T-Shirt",
"id": "CLOTH005",
"price": 10.00,
"category": "Clothing"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/6",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Jacket",
"id": "CLOTH006",
"price": 20.00,
"category": "Clothing"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/7",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Bookcase",
"id": "FURN001",
"price": 40.00,
"category": "Furniture"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/8",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Coffee Table",
"id": "FURN002",
"price": 50.00,
"category": "Furniture"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/9",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Vanity",
"id": "FURN003",
"price": 90.00,
"category": "Furniture"
},
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "https://:${serverPort}/api/products/10",
"hreflang": "en",
"type": "application/hal+json"
}
},
"name": "Table Saw",
"id": "TOOL001",
"price": 120.00,
"category": "Tools"
}
],
"count": 13,
"max": 10,
"offset": 0,
"sort": null,
"order": null
}向 next 链接 https://:8080/product/index?offset=10&max=10 发出请求,您将看到下一页结果。由于我们样本数据中的资源数量较少,因此只有 2 页 - 尝试将请求中的 max 参数更改为 4 - 您现在将检索更多页面,以反映更小的页面大小。
如果您愿意,请重复这些步骤,为其他领域资源启用分页,例如 Order 和 Customer。
5.5 自定义 MIME 类型
HAL 资源可以声明客户在与 API 交互时应使用的自定义“MIME 类型”(或“内容类型”)。Grails 在默认的 application.yml 中包含了两种通用的 HAL MIME 类型
accept:
header:
userAgents:
- Gecko
- WebKit
- Presto
- Trident
types:
json:
- application/json
- text/json
hal:
- application/hal+json
- application/hal+xml
xml:
- text/xml
- application/xml如果你愿意,可以通过向此配置添加条目为你的 API 指定自定义 MIME 类型
xml:
- text/xml
- application/xml
atom: application/atom+xml
css: text/css
csv: text/csv
js: text/javascript
rss: application/rss+xml
text: text/plain
all: '*/*'
inventory: "application/vnd.com.example.inventory+json" (1)
urlmapping:
cache:
maxsize: 1000| 1 | 指定了一种名为 inventory 的 MIME 类型,并为其提供类型规范(根据惯例,vnd 指示“vendor”MIME 类型) |
现在你可以在 JSON 视图中使用 type 帮助器方法使用这种自定义 MIME 类型
import com.example.Product
model {
Product product
}
json {
hal.links(product)
hal.embedded(category: product.category)
hal.type("inventory") (1)
id product.inventoryId
name product.name
price product.price
}| 1 | hal.type() 方法接受一个字符串来标识 application.yml 文件中的自定义 MIME 类型或一个明确的 MIME 规范作为一个字符串 |
向 https://:8080/api/products/1 发出请求以查看自定义内容类型
$ curl -i localhost:8080/product/1
HTTP/1.1 200
X-Application-Context: application:development
Content-Type: application/vnd.com.example.inventory+json;charset=UTF-8 (1)
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Date: Sun, 05 Feb 2017 01:51:08 GMT
def result = render(view: "/product/show", model:[product: product])
then:
result.json._embedded
}
}| 1 | 注意 Content-Type 头中的新 MIME 类型 |
6 探索 API
HAL+JSON 是用于构建 API 输出的灵活而强大的规范。它允许你的 API 的客户(无论是第三方集成还是你自己的 Web 应用或原生应用)以高效且一致的方式导航你的资源。
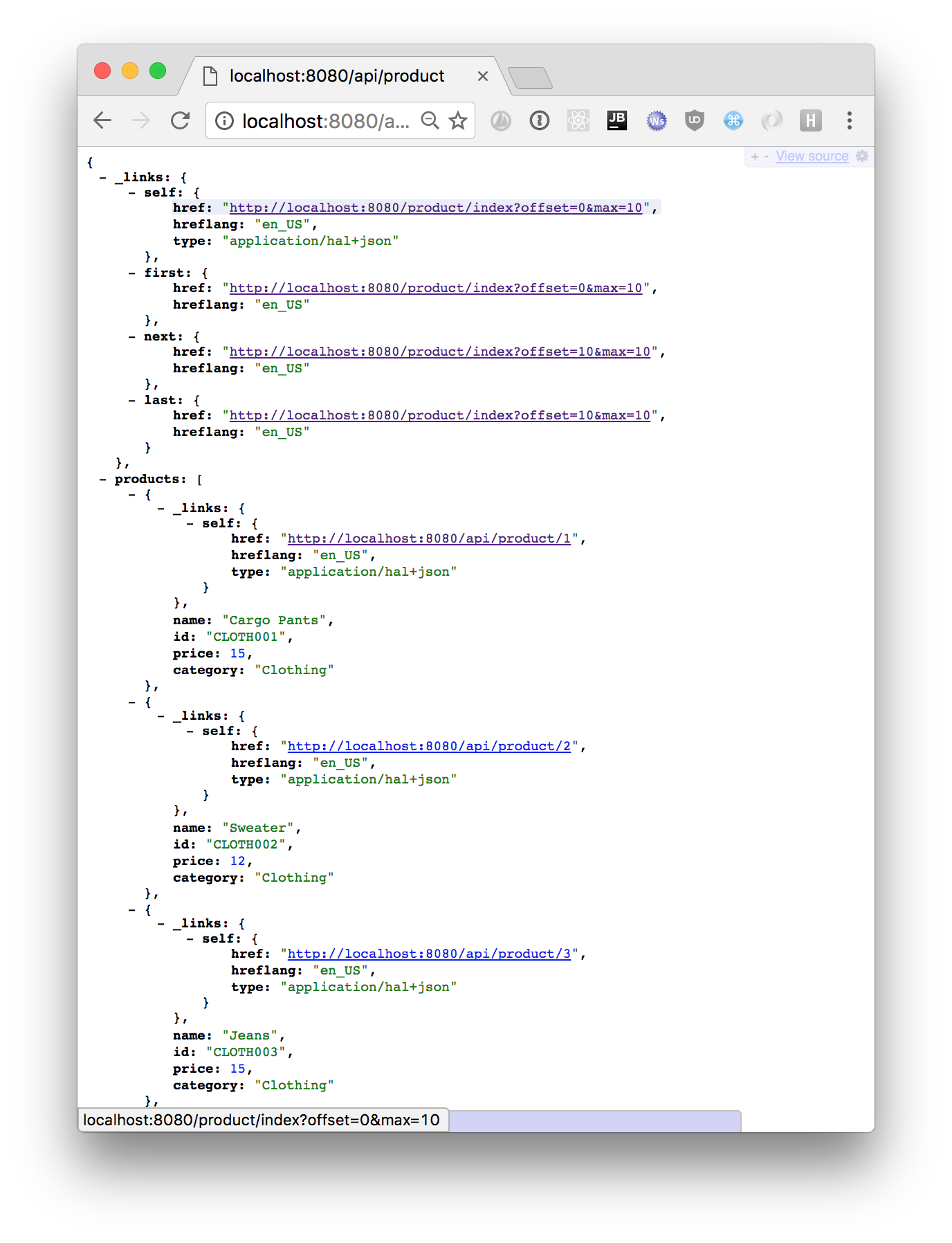
有许多有用的工具可用于开发和测试 HAL+JSON API。如果你使用 Google Chrome 浏览器,请尝试安装 JSONView 插件,并将你的浏览器导航到 https://:8080/api/products。此插件会以美观格式呈现 JSON,并允许你在浏览器中跟踪资源之间的链接。
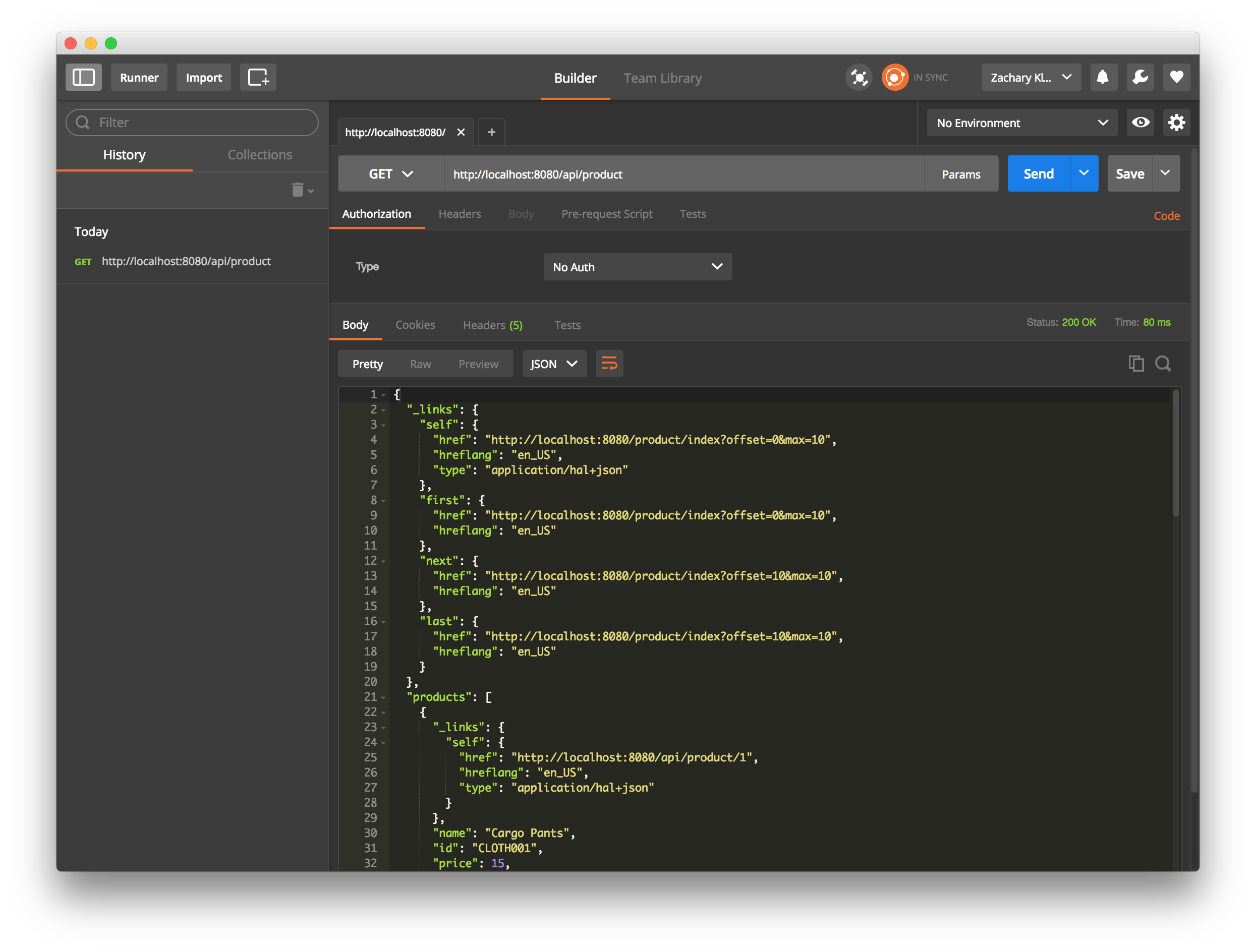
用于测试和检查 API 的另一个强大工具是 Postman,这是一种适用于 macOS、Windows、Linux 和 Chrome OS 的基于 Google Chrome 的应用。